A mineralogical and geochemical assessment of the As-, Cu-, In-, Pb-, Sb- and Zn- rich mine wastes at Pefka epithermal deposit in Evros, Greece = Ορυκτολογική και γεωχημική μελέτη των αποβλήτων που είναι πλούσια σε As-, Cu-, In-, Pb-, Sb- και Zn στην επιθερμική μεταλλοφορία στα Πεύκα Έβρου, Ελλάδα.
Περίληψη
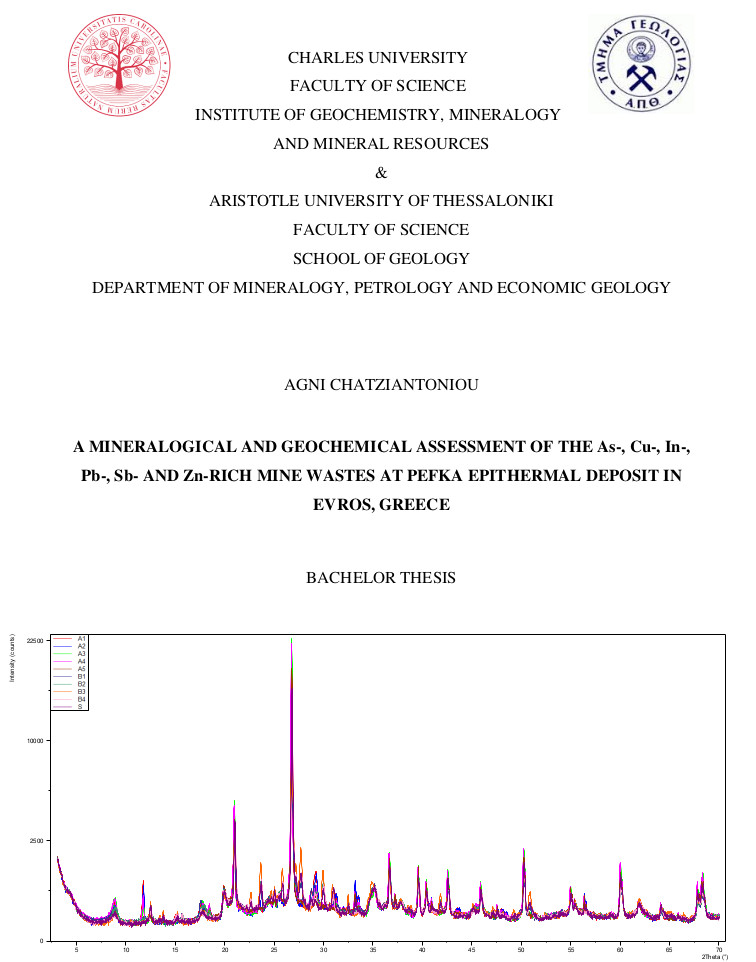
The aim of this research is to analyze the presence of As, Cu, In, Pb, Sb and Zn in the mine wastes of this epithermal system, observe the secondary mineral phases of these elements and evaluate their potential mobility in the waste material. To succeed this, a detailed geochemical and mineralogical study was carried out, by processing ten samples, collected from three different locations of the Pefka area (A1-A5, B1-B4, S). The methods that were used for this study were: geochemical [X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis, pH measurements, mineralization and quantitative chemical analysis, sequential extraction (SE) analysis] and mineralogical [X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) analysis, Electron Probe Microanalysis (EPMA)]. The sequential extraction, XRD analysis and microprobe analysis were applied for selected samples, which were found by XRF to have special interest, chemically and mineralogically. This multi-method data set was combined to reach the final conclusions.
Τα Πεύκα αποτελούν μια ενδιάμεσης (IS) ως υψηλής (HS) θείωσης πολυμεταλλική μεταλλοφορία της βορειοανατολικής Ελλάδας. Σύμφωνα με τη δημοσίευση του Dimou et al. (1994) η οποία βασίστηκε στις ορυκτολογικές και γεωχημικές αλλοιώσεις των πετρωμάτων, η ορυκτοποίηση στην περιοχή των Πεύκων αποτελεί ένα επιθερμικό σύστημα με υψηλή κατάσταση θείωσης. Συγκεκριμένα, η ορυκτοποίηση είναι υψηλά εμπλουτισμένη σε χαλκό (πάνω από 1 wt%) και ίνδιο (περίπου 700 ppm) και αποτελείται από δύο συστήματα εγκάρσιων φλεβών με ενδιάμεση (IS) και υψηλή (HI) κατάσταση θείωσης, τα οποία εντοπίζονται σε ανδεσιτικές λάβες (Voudouris et al. 2021). Η εξόρυξη στα Πεύκα, με φρέατα, υπόγειες στοές και επιφανειακές εργασίες δραστηριοποιήθηκε τη δεκαετία του 1950, αλλά έκτοτε δεν έγινε καμία περιβαλλοντική αποκατάσταση.
Σκοπός της παρούσας έρευνας είναι η ανάλυση της παρουσίας As, Cu, In, Pb, Sb, και Zn στα απόβλητα αυτού του επιθερμικού συστήματος, η παρατήρηση των δευτερογενών ορυκτών φάσεων αυτών των στοιχείων και η αξιολόγηση της πιθανής κινητικότητάς τους στα απόβλητα. Για να επιτευχθεί αυτός ο σκοπός, πραγματοποιήθηκε μια λεπτομερής γεωχημική και ορυκτολογική μελέτη, με την επεξεργασία δέκα δειγμάτων, τα οποία συλλέχθηκαν από τρεις διαφορετικές τοποθεσίες της περιοχής των Πεύκων (A1-A5, B1-B4, S). Οι μέθοδοι που χρησιμοποιήθηκαν για τη μελέτη αυτή ήταν: γεωχημική ανάλυση [φθορισμός ακτίνων X (XRF), μετρήσεις pH, ορυκτοποίηση και ποσοτική χημική ανάλυση, ανάλυση διαδοχικής εκχύλισης (SE)] και ορυκτολογική [ανάλυση περίθλασης ακτίνων X (XRD), μικροανάλυση ηλεκτρονικής ανίχνευσης (EPMA)]. Η ανάλυση διαδοχικής εκχύλισης, η ανάλυση XRD και η ανάλυση μικροανίχνευσης εφαρμόστηκαν για επιλεγμένα δείγματα, τα οποία, διαπιστώθηκε από το XRF, ότι παρουσιάζουν ιδιαίτερο ορυκτολογικό και γεωχημικό ενδιαφέρον. Τα δεδομένα αυτών των πολλαπλών μεθόδων συνδυάστηκαν για την εξαγωγή των τελικών συμπερασμάτων.
Πλήρες Κείμενο:
PDFΑναφορές
Arikas, K., Voudouris, P., (1998). Hydrothermal alterations and mineralizations of magmatic rocks in the southern Rhodope Massif, Acta Vulcanologica 10(2), 353-365.
Ashworth, K. L., Billet, M. F., Constantinidis, D., Demetriades, A., Katirtzoglou, C., Michael, C., (1988). Base metal mineralization in the Evros region Thrace, N. E. Greece, part of the Special Publication of the Society for Geology Applied to Mineral Deposits book series (MINERAL DEPOS.,volume 5),
Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 169-181. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-02538-3_11
Bonev, N., Stampfli, G., (2008). Gabbro, plagiogranite, and associated dykes in the supra-subduction zone Evros Ophiolites, NE Greece, Geological magazine 146, 72-91. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016756808005396
Caracciolo, L., Critelli, S., Cavazza, W., (2014). The Rhodope Zone as a primary sediment source of the southern Thrace basin (NE Greece and NW Turkey): evidence from detrital heavy minerals and implications for central-eastern Mediterranean palaeogeography. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-014-1111-9
Castaing, R., (1960). Electron Probe Microanalysis, Advances in Electronics and Electron Physics 13, 317-386. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2539(08)60212-7
Dimou, E., Michael, K., Serment, R., (1994). Mineralogical composition of the epithermal- polymetallic ore of Pefka, Rhodope.
Dold, B., (2003). Speciation of the most soluble phases in a sequential extraction procedure adapted for geochemical studies of copper sulfide mine waste, Journal of Geochemical Exploration 80, 55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(03)00182-1
Drahota, P., Grösslová, Z., Kindlová, H., (2014). Selectivity assessment of an arsenic sequential extraction procedure for evaluating mobility in mine wastes. Analytica Chimica Acta 839, 34–43.
Drahota, P., Knappova, M., Kindlova, H., Culka, A., Majzlan, J., Mihaljevic, M., Rohovec, J., Veselovsky, F., Fridrichova, M., Jehlicka, Jan., (2016). Mobility and attenuation of arsenic in sulfide- rich mining wastes from Czech Republic, Science of the total environment, 192-203, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.079
Epp, J., (2016). 4 - X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques for materials characterization, Materials Characterization Using Nondestructive Evaluation (NDE) Methods, 81-124. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100040-3.00004-3
Ettler, V., Jarosikova, A., Mihaljevic, M., Kribek, B., Nyambe, I., Kamona, F., Mapani, B., (2020). Vanadium in slags from smelting of African Pb-Zn vanadate ores: Mineralogy, extractability, and potential recovery, Journal of geochemical exploration, 106631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106631
Ettler, V., Mihaljevic, M., Drahota, P., Kribek, B., (2022). Cobalt-bearing copper slangs from Luanshya (Zambian Copperbelt): Mineralogy, geochemistry, and potential recovery of critical metals, Journal of geochemical exploration, 106987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2022.106987
Kabata-Pendias, A., (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants, 4th edition.
Karimian, N., Johnston, S. G., Burton, E. D., (2017). Antimony and arsenic partitioning during Fe(II)- induced transformation of jarosite under acidic conditions. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.106
L.-E. Ricou, J.-P. Burg, I. Godfriaux & Z. Ivanov (1998). Rhodope and Vardar: the metamorphic and the olistostromic paired belts related to the Cretaceous subduction under Europe, Geodinamica Acta, 11:6, 285-309. https://doi.org/10.1080/09853111.1998.11105326
Marchev, P., Kaiser- Rohrmeier, M., Heinrich, C., Ovtcharova, M., Quadt, von A., Raicheva, R., (2005): Hydrothermal ore deposits related to post-orogenic extensional magmatism and core complex formation: The Rhodope Massif of Bulgaria
and Greece, Ore Geology Reviews 27, 53-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.07.027
Melfos, V., Voudouris, P., (2012). Geological, Mineralogical and Geochemical Aspects for Critical and Rare Metals in Greece, Minerals 2(4), 300-317. https://doi.org/10.3390/min2040300
Melfos, V., Voudouris, P., (2017). Cenozoic metallogeny of Greece and potential for precious, critical, and rare metals exploration, Ore Geology Reviews 89, 1030-1057. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.05.029
Michael, C. (2004). EPITHERMAL SYSTEMS AND GOLD MINERALIZATION IN WESTERN THRACE (NORTHERN GREECE). Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece, 36(1), 416–423. https://doi.org/10.12681/bgsg.16727
Naden, J, Kilias, S. P, Darbyshire, D. P. F., (2005). Active geothermal systems with entrained seawater as modern analogs for transitional volcanic-hosted massive sulfide and continental magmato-hydrothermal mineralization: The example of Milos Island, Greece, Geology, 541–544. https://doi.org/10.1130/G21307.1
Nesbitt, R. W., Billett, M. F., Ashworth, K. L., Deniel, C., Constantinides, D., Demetriades, A., Katirtzoglou, C., Michael, C., Mposkos, E., Zachos, S.,
Sanderson, D., (1988). The geological setting of base mineralization in the Rhodope region, northern Hellas, Mineral Deposits within the European Community, 499-514.
Nordstrom, D.K., (1977). Thermochemical redox equilibria of Zobell’s solution, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 41, 1835–1841. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(77)90215-0
Pansu, M., Gautheyrou, J., (2006). Handbook of Soil Analysis: Mineralogical, Organic and Inorganic Methods. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg 2006. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-31211-6
Papanikolaou, D., Panagopoulos, A., (1981). On the structural style of the Southern Rhodope, Greece, Geologica Balcanica 11, 13-22.
Passos, E. de A. et. Al., (2010). Assessment of trace metals contamination in estuarine sediments using a sequential extraction technique and principal component analysis, Microchemical Journal 96, 50-57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2010.01.018
Pirajno, F., (2009). Hydrothermal Processes and Mineral Systems, Springer Science and Business Media LLC.
Tilley, D., (2021). Epithermal gold deposits, Geology for investors.
Tombros, S., Seymour, St. K., Williams-Jones, A. E., Spry, P.G., (2007). The Genesis of Epithermal Au-Ag-Te Mineralization, Panormos Bay, Tinos Island, Cyclades, Greece, Economic Geology 102(7):1269-1294. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.102.7.1269
Ure, A.M., (1996). Single extraction schemes for soil analysis and related applications, Science of the Total Environment 178, 3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(95)04791-3
Varshneya, K. A, Mauro, J. K., (2019). Fundamentals of Inorganic Glasses (Third edition). https://doi.org/10.1016/C2017-0-04281-7
Voudouris, P., Repstock, A., Spry P.G., Frenzel, M., Mavrogonatos, C., Keith, M., Tarantola, A., Melfos, Va., Tombros, St., Zhai, D., Cook, N. J.,
Ciobanu, C. L., Schaarschmidt, A., Rieck, B., Kolitsch, U., Falkenberg, J., (2022). Physicochemical constraints on indium-, tin-, germanium-, gallium-, gold-, and tellurium-bearing mineralizations in the Pefka and St Philippos polymetallic vein- and breccia-type deposits, Greece, Ore Geology Reviews, 104348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104348
Warr, L.N., (2021). IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols, Mineralogical Magazine 85, 291–320. https://doi.org/10.1180/mgm.2021.43
White, N. C., Hedenquist, J. W., (1989). Epithermal environments and styles of mineralization: Variations and their causes, and guidelines for exploration, Journal of geochemical exploration 36, 445-474. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6742(90)90063-G
Εισερχόμενη Αναφορά
- Δεν υπάρχουν προς το παρόν εισερχόμενες αναφορές.
